The following page of notes will cover:
- Finishes
- Paper and board finishes
Paints:
- Stops rusting/corrosion
- Aesthetically pleasing
- Range of colours
- Saves time/money
|
- Chips/flakes away
- Environmently unfriendly
|
Uses: Bridges, metal work, brick work
Varnishes:
- Protects from dirt/sunlight/water
- Enhances look of wood
- Easy to apply
- Can't see brush strokes
|
- Can be dull colour
- Bubbles can ruin finished look
- Some varnishes are bad for the environment (brushes cleaned result in varnish into water system)
|
Uses: Hardwoods and sodtwoods
Sealant:
- Waterproof finish
- Thermal/acoustical insulation
- Electrical insulation
- Used for simple smoothing/filling
|
- Does not have great strength
|
Uses: Pipe threads, aquariums, roofs, hydraulic systems
Preservatives:
- Improves lifespan of timber
- Reduce biological corrosion
- Improves aesthetics of wood
|
- Toxic
- More effective if used to pressure treat wood
|
Uses: Wood products exposed to water and corrosion
Anodising:
How it works:
- Used to add a coating to aluminium
- An electric current is passed through an acidic electrolyte
- The metal being protected (anode) then builds a layer of aluminium oxide
- Can be done in a range of colours
- Very durable finish
- Hard finish/scratch resistant
- Thin finish - doesn't block holes in product
- Heat resistant finish
|
- Joining/machining can't be done after anodising
- Expensive
|
Uses: Window frames, bike frames
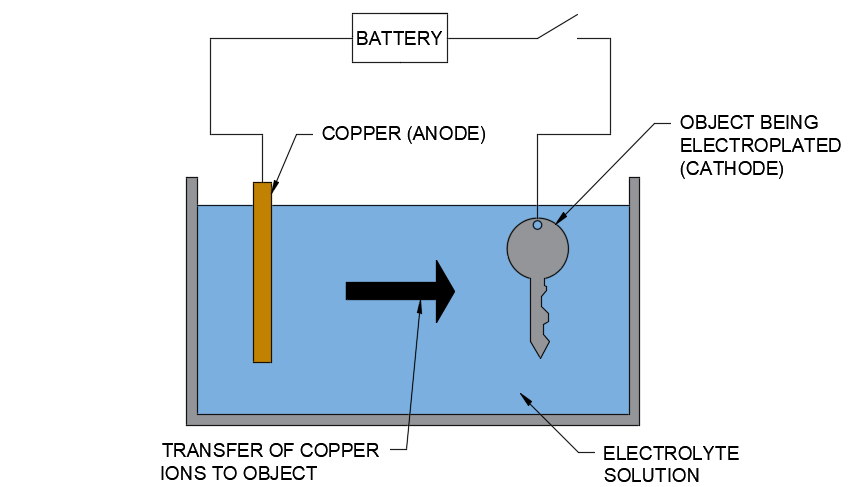
Electro-plating:
How it works:
- A cheap metal is coated onto a metal to protect it
- An electric current is passed through an acidic electrolyte
- The metal being protected (anode) then builds a layer of metal oxide
- Corrosion resistant
- Easy to do
- Improves mechanical properties
- Improves aesthetics appeal
- Cost effective
- Durable finish
|
- Time consuming
- Toxic fumes released
- Non-unifrom finish
|
Uses: Spoons, taps, shower heads
Powder coating:
How it works:
- The metal is heated to 230 degrees
- The metal is then dipped into polymer powder
- The polymer coating is then allowed to cool
- Range of colour finishes
- Non-toxic
- Evenly coated finish
- More protective than paint
- Better for environment that paint
|
- Harder to do than paint
- Uses energy/needs energy for heating powder (unlike paint)
|
Uses: Cars, wheel arches, sports equipment
Oil coating:
- Replaces oils in wood lost as timber dries out
- Hard wearing
- Protective finish
|
- Multiple layers needed to be applied
- Time consuming
- Labour intensive
|
Uses: Teak oil used on woods to give better protection
Galvanisation:
How it works:
- The metal is dipped into molten zinc
- The zinc acts as a sacrifical anode to protect metal underneath
- Prevents rusting/corrosion
- Simple process
- Quick process that can be done on a mass production scale
|
- Zinc layer can be chipped away over time
- Not a very aesthetic finish
|
Uses: Bridges, pipes, metal brackets
Cathodic protection (Impressed current and sacrifical anode):
How it works (Impressed current):
- Metal is connected to electric power supply which is connected to a cathode
- The cathode rusts over time whilst the anode (metal being protected) remains intact
How it works (Sacrifical anode):
- A metal which is more reactive is connected to the metal being protected
- The more reactive metal (sacrifical anode) rusts over time whilst the metal being protected remains intact
- Proetcts structures that are buried in dirt/water
- Greatly increases lifespan of metal being protected
- Cost efficent to run
|
- Hard to install
- Complex to upkeep
- Uses energy/needs connection for impressed current
- Expensive to install
|
Uses: Pipelines, ships, cars
Laminating:
How it works:
- Coating the paper with liquid/film to protect it
- Aesthetic/high quality look
- Rigid/strengthens paper
- Low cost
- Hard to tear/rip
|
- Paper hard to access/write on
|
Uses: Posters, pictures, song music
Varnishing:
How it works:
- Clear, non-pigmented ink used on pre-coated papers
- Enhances the colour of paper
- Protects against dirt/fingerprints
|
- Long dry time
- Slows down overall completion time - slower production rate
- Sticks to other surfaces/pages if not fully dried
|
Uses: Brochures, magazines
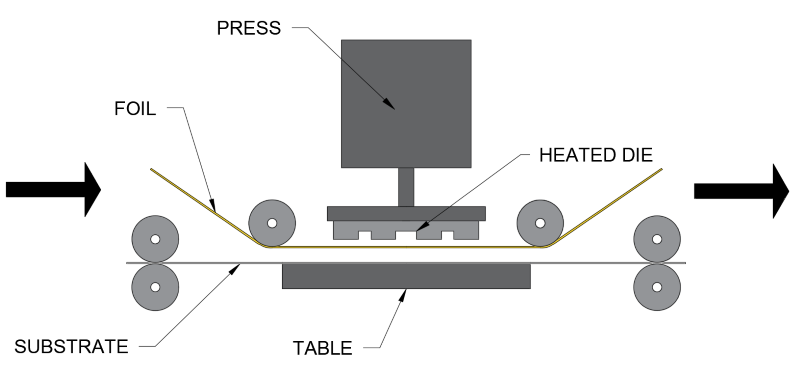
Hot foil blocking:
How it works:
- A foil sheet is place between the paper and the die
- The die is then pressed onto the foil and heated to allow the foil to join to the paper
- The die is then removed and the foil cools
- Enhances/adds value to paper
- Improved aesthetics
- Range of colours/foils etc
|
- If heated for too long the foil can bubble and melt
- If heated not long enough the foil will not stick
- Difficulty in reproducing tints and halftones
|
Uses: Passports, gold foil decorations, wedding invite cards
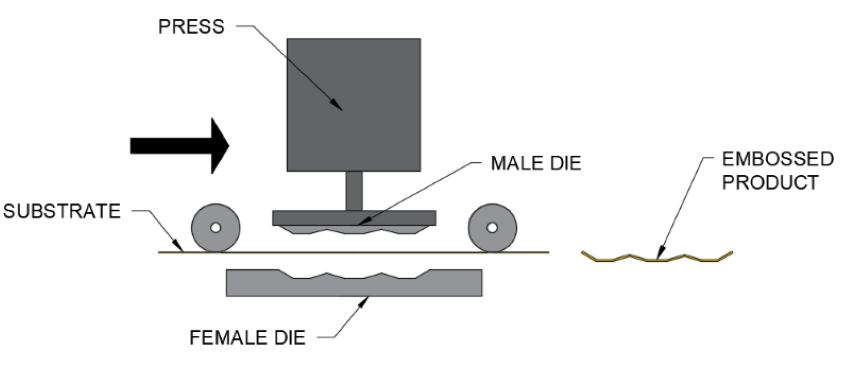
Embossing:
How it works:
- The paper is placed between the two formers
- The formers then close around the paper to form the shape
- Formers can be heated/cold
- High quality finish
- Sophisticated appearance
|
|
Uses: Toblerone card packaging, birthday cards
Topic test: